Naxos (island)
| Naxos Νάξος |
|
|---|---|
 The City of Naxos |
|
| Geography | |
| Island chain: | Cyclades |
| Area: | 429.785 km² (166 sq.mi.) |
| Highest mountain: | Mt. Zas (999 m (3,278 ft)) |
| Government | |
| Periphery: | South Aegean |
| Prefecture: | Cyclades |
| Capital: | Naxos (city) |
| Statistics | |
| Population: | 18,188 (as of 2001) |
| Density: | 42 /km² (110 /sq.mi.) |
| Postal code: | 843 xx |
| Area code: | 22850 |
| License code: | EM |
Naxos (in Greek, Νάξος) is a Greek island, the largest island (429 km2 (166 sq mi)) in the Cyclades island group in the Aegean. It was the centre of archaic Cycladic culture.
The island comprises the two municipalities of Naxos and Drymalia. The largest town and capital of the island is Hora or Naxos City, with 6,533 inhabitants (2001 census). The main villages are Filoti, Apiranthos, Vivlos, Agios Arsenios, Koronos and Glinado.
Naxos is a popular tourist destination, with several easily accessible ruins. It has a number of beautiful beaches, such as those at Agia Anna, Agios Prokopios, Alikos, Kastraki, Mikri Vigla, Plaka, and Agios Georgios, most of them near Hora. Naxos is the most fertile island of the Cyclades. It has a good supply of water in a region where water is usually inadequate. Mount Zas (999 metres) is the highest peak in the Cyclades, and tends to trap the clouds, permitting greater rainfall. This has made agriculture an important economic sector with various vegetable and fruit crops as well as cattle breeding, making Naxos the most self sufficient island in the Cyclades. Naxos is also known within Greece for its potatoes.
Contents |
Mythic Naxos
According to a story in Greek mythology, the young Zeus was raised in a cave on Mt. Zas ("Zas" meaning "Zeus"). Homer mentions "Dia"; literally the sacred island "of the Goddess". Karl Kerenyi explains (speaking as if he were an ancient Greek):
| “ | This name, Dia, which means 'heavenly' or 'divine', was applied to several small craggy islands in our [ Aegean ] sea, all of them lying close to larger islands, such as Crete or Naxos. The name "Dia" was even transferred to the island of Naxos itself, since it was more widely supposed than any other to have been the nuptial isle of Dionysus. (Kerenyi 1951 pp. 271–272) | ” |
One legend has it that in the Heroic Age before the Trojan War, Theseus abandoned the princess Ariadne of Crete on this island after she helped him kill the Minotaur and escape from the Labyrinth. Dionysus (god of wine, festivities, and the primal energy of life) who was the protector of the island, met Ariadne and fell in love with her. But eventually Ariadne, unable to bear her separation from Theseus, either killed herself (according to the Athenians), or ascended to heaven (as the older versions had it). The Naxos portion of the Ariadne myth is also told in the Richard Strauss opera Ariadne auf Naxos.
The giant brothers Otus and Ephialtes figure in at least two Naxos myths: in one, Artemis bought the abandonment of a siege they laid against the gods, by offering to live on Naxos as Otus's lover; in another, the brothers had actually settled Naxos.
History
Greek and Byzantine Naxos
During the 8th and 7th centuries, Naxos dominated commerce in the Cyclades.
Revolt of Naxos
Herodotus describes Naxos circa 500 BCE as the most prosperous Greek island.[1]
In 502 BC an unsuccessful attack on Naxos by Persian forces led several prominent men in the Greek cities of Ionia to rebel against the Persian Empire in the Ionian Revolt, and then to the Persian War between Greece and Persia.
The Dukes of Naxos
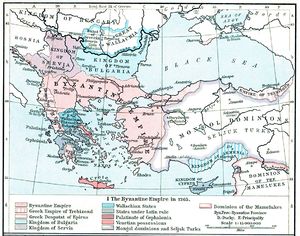
In the aftermath of the Fourth Crusade, with a Latin Emperor under the influence of the Venetians established at Constantinople, the Venetian Marco Sanudo conquered the island and soon captured the rest of the islands of the Cyclades, establishing himself as Duke of Naxia, or Duke of the Archipelago. Twenty-one dukes in two dynasties ruled the Archipelago, until 1566; Venetian rule continued in scattered islands of the Aegean until 1714. Under Venetian rule the island was called Italian: Nasso.
Ottoman Naxos (1564-1821)
The Ottoman administration remained essentially in the hands of the Venetians; the Porte's concern was satisfied by the returns of taxes. Very few Turks ever settled on Naxos, and Turkish influence on the island is slight. Under Turkish rule the island was known as Turkish: Nakşa. Turkish sovereignty lasted until 1821, when the islands revolted; Naxos finally became a member of the Greek state in 1832.
Historical population
| Year | Island population | Change |
|---|---|---|
| 1981 | 14,037 | - |
| 1991 | 14,838 | +801/+5.71% |
| 2001 | 18,188 | +3,350/+22.58% |
Notable people
- Manolis Glezos (1922-) politician, writer
- Iakovos Kambanelis (1922-) poet, playwright, lyricist and novelist
- Nicodemus the Hagiorite (1749–1809), saint
- Petros Protopapadakis (1854–1922) Prime Minister of Greece
- Thanasis Polykandriotis musician,bouzouki expert and composer
- Spyros Papadopoulos actor
- Giorgos Ninios actor
- Halkou Irini(Halkorini) poet
- Stelios Manolas football player
- Kostas Manolas football player
- Giannis Kontoes football player
- Efkartidis (7th century b.C.), sculpter
- Markelos - Michail Kontopidis (1651–1716), medical philoshopher
- Methodios from Antioch (Patriarch)
- Nikolaos Planas (1851–1932), saint
- Anthimos the Third (1762–1842), Patriarch of Constantinople
- Ioannis Sakellion (1815–1891), Scholar, principal of Patmos' School
- Εleftherios Kastrisios (1843–1931), Military Dean
- Antonios Magkakis (1890–1952), politician, father of politician Alexandros Magkakis
- Iakovos Vazeos, Lieutenant
- Emmanouel Dris , Deputy Dean of the National Technical University
- Stylianos Korres (1910–1989), Dean, Founder of the Company of Cycladic Studies
- Nikos Sfiroeras (1913), Litterateur, Poet
- Vasilis Sfiroeras (1921), Proffesor in the University of Athens
- Manos Chorianopoulos (1925–2007), Reporter
- Iakovos Psarras (1936–2006), actor
- Keti Chomata, Singer
- Manolis Korres, Acropolis' restorator, Professor of Architecture in the National Technical University
See also
- Communities of the Cyclades
- Emery (mineral) mined on Naxos, the main source of supply for the ancient world, since antiquity
References
- Kerenyi, Karl 1951. The Gods of the Greeks.
External links
- official website (German) (Greek) (English)
|
|||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||